First, the grinding process mechanism
Precision grinding is a free abrasive cutting process. It is used to inject abrasive into a rigid rig (such as cast iron, tin, aluminum and other soft metals or hardwoods, plastics, etc.), and under the constant pressure, through the relative movement of the rig and the workpiece, The micro-cutting action of the abrasive particles removes trace amounts of workpiece material to achieve advanced geometric accuracy and excellent surface roughness.
1. The processing model for grinding hard and brittle materials of hard and brittle materials is shown in Figure 3-8. A part of the abrasive grains are micro-cut by the surface of the workpiece with the exposed tip under the action of the grinding pressure; the other part of the abrasive grains produces a rolling effect, causing the surface of the workpiece to be brittle and chipped to form chips. The abrasive grains are 1 μm of alumina, silicon carbide, or the like.
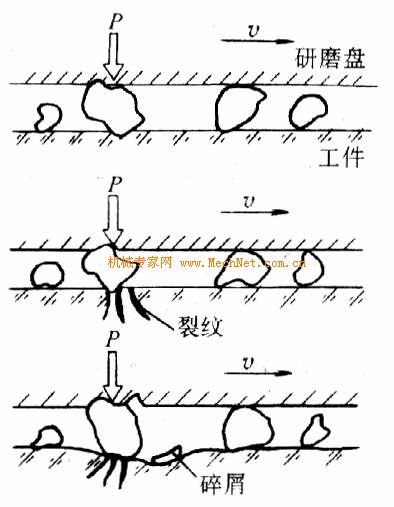
2. Grinding of a metal material When grinding a metal material, the grinding action of the abrasive grains is equivalent to a state in which the cutting depth of ordinary cutting and grinding is extremely small, and no crack is generated. Since the abrasive grains are in a free state, it is difficult to form a continuous cutting, and only the intermittent grinding action between the abrasive grains and the workpiece forms the wear debris.
Second, the polishing process mechanism polishing refers to the use of low-speed rotating soft elastic or viscoelastic materials (plastic, asphalt, paraffin, tin, etc.) polishing disc, or high-speed rotating low-elastic material (cotton, felt, artificial leather, etc.) polishing disc, A polishing agent is added, which has a certain abrasive property to obtain a smooth surface. Polishing—cannot improve the shape accuracy and dimensional accuracy of the workpiece. The abrasive grains used for polishing are fine abrasive grains of 1 μm or less.
The polishing model is shown in Figure 3-9. The minute abrasive grains are elastically held by the polisher to grind the workpiece, so that the force of the abrasive grains on the workpiece is small, and cracks do not occur even if the brittle material is polished.
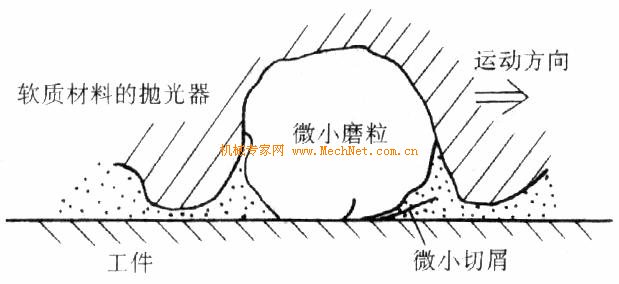
Polishing is a combination of the tiny plastic cutting action of the abrasive particles and the chemical dissolution of the processing fluid.
Third, the main process factors of precision grinding, polishing The main process factors of precision grinding and polishing are shown in Table 3-5.
Within a certain range, increasing the grinding pressure can improve the grinding efficiency.
In addition, ultra-precision grinding has the following basic requirements for the grinding motion trajectory, and the cutting conditions and cutting conditions of the workpiece machining surface and the lap surface are the same or similar:
1 The workpiece moves parallel to the plane of the grinding disc, so that the points on the workpiece have the same or similar grinding stroke.
2 Any corner on the workpiece to ensure smooth grinding movement.
4 Ensure that the workpiece travels all over the surface of the grinding disc so that the grinding disc wears evenly, thus ensuring the flatness of the surface of the workpiece.
5 Change the moving direction of the workpiece in time to reduce the surface roughness and ensure the surface is uniform.
4. Grinding Disc and Polishing Disc 1. Grinding Disc The grinding disc is a carrier for coating or embedding abrasives to exert abrasive cutting action and at the same time is a forming tool for grinding the surface. Grinding requires a high degree of geometric accuracy for the machined surface of the grinding disc.
The hardness of the grinding disc material is lower than the hardness of the workpiece material, and the structure is uniform and compact, free from impurities, foreign matter, cracks and defects, and has certain abrasive embedding and impregnation properties. Commonly used grinding disc materials are cast iron, brass, glass, and the like.
The structure of the grinding disc should have good rigidity, precision retention, wear resistance, chip evacuation and heat dissipation. In order to obtain a good abrasive surface, grooves are often formed on the surface of the grinding disc. The purpose of slotting is:
1 Store excess abrasive particles in the tank to prevent abrasive buildup and damage the surface of the workpiece.
2 As a passage for supplying abrasive grains to the workpiece during processing.
3 As a channel for timely chip removal to prevent the abrasive surface from being scratched.
The fixed abrasive grinding disc is a kind of grinding tool suitable for precision grinding of brittle materials such as ceramics, silicon wafers and crystals, and has the advantages of good surface precision retention and high grinding efficiency. It is a method of mixing diamond or cubic boron nitride abrasive with cast iron powder, sintering it into small pieces, or fixing the abrasive grains on the metal foil by electroforming, and then bonding these small pieces to the grinding disk with epoxy resin. And made.
2. Polishing plate polishing plate plane accuracy and precision retention is the key to achieve high-precision plane polishing. Therefore, when polishing a small-area high-precision planar workpiece, a polishing disc having a small elastic deformation and always maintaining a flatness is used. It is desirable to use a special glass or a layer of elastic material or soft metal material as a polishing disk on a flat metal plate.
In order to obtain a smooth surface without damage, when the workpiece material is soft (such as processing optical glass), semi-soft polishing discs (such as tin plates, lead plates) and soft polishing discs (such as asphalt discs, paraffin discs) can be used. The advantage of using a soft polishing disc is that the polished surface finish layer and surface roughness values ​​are small; the disadvantage is that it is difficult to maintain flatness and thus affect the flatness of the workpiece.
5. Abrasives and polishing agents Basic requirements for abrasive grains: 1 uniform shape and size; 2 can be properly broken to make the cutting edge sharp; 3 melting point is higher than the melting point of the workpiece; 4 is easy to disperse in the polishing liquid. For the abrasive particles for polishing powder, in addition to the above requirements, the chemical activity acting on the workpiece material is also considered.
The main function of the grinding and polishing fluid is to cool, lubricate, uniformly grind the surface of the disc and remove debris. Requirements for grinding and polishing liquid: 1 Effective heat dissipation to prevent thermal deformation of the grinding disc and workpiece; 2 low adhesion to ensure the fluidity of the abrasive; 3 no contamination of the workpiece; 4 physical and chemical properties are stable, no decomposition and deterioration; It can disperse the abrasive grains well.
6. Non-contact polishing Non-contact polishing refers to a polishing method in which the workpiece and the polishing disk are not in contact with each other during polishing, and the polishing agent is used to impact the surface of the workpiece to obtain a perfect crystallinity and precise shape of the processed surface, and the removal amount is only a few More than a dozen atomic levels. Non-contact polishing is mainly used for functional crystal material polishing (focusing on crystal integrity and physical properties) and polishing of optical parts (focusing on surface roughness and shape accuracy).
1. Elastic Emission Machining (EEM) refers to the fact that the lap and the workpiece do not touch each other during processing. The particles are impacted on the surface of the workpiece by the particles, causing elastic damage to the atomic bonding of the substance. The workpiece is removed at the atomic level. Material to obtain a non-damaged machined surface.
The principle of elastic emission processing is to accelerate the fine abrasive particles by water flow, impact the surface of the workpiece with the incident angle (approx. level) as small as possible, generate instantaneous high temperature and high pressure at the contact point, and solid phase reaction occurs, resulting in the vacancy of the atomic lattice of the surface layer of the workpiece. The workpiece atoms and the abrasive particles mutually diffuse to form impurity point defects which are weakly bonded to other atoms in the surface layer of the workpiece. When these defects are again hit by the abrasive grains, the impurity point atoms are removed together with the adjacent several atoms. At the same time, the atoms protruding from the surface of the workpiece are also removed due to the large shear force.
The elastic emission processing method is shown in Figure 3-10. The processing head is a polyurethane ball. In the microparticle suspension, the processing ball head approaches the surface of the workpiece in the rotation, so that the particles in the suspension act in a small area (Ф1~2 mm) on the surface of the workpiece.
Numerical control is performed on the machining head and the worktable to realize surface machining. The ECM CNC machining device is shown in Figure 3-11.
2. Float Polishing is a non-contact ultra-precision polishing method with extremely high flatness. The floating polishing device is shown in Figure 3-12. The high-rotation precision polishing machine uses a high-flatness plane with a tin-polished disc with concentric circles or spiral grooves. The polishing liquid covers the entire surface of the polishing disc, and the polishing disc and the workpiece are polished at high speed. The liquid is in a state of dynamic pressure fluid and forms a liquid film to polish the workpiece in a floating state. The production of ultra-precision polishing discs is the key to floating polishing.
3. Dynamic pressure floating polishing (Hydrodynami-type Polishing) is another non-contact polishing. The flat non-contact polishing device is shown in Figure 3-13. The working principle is: when a disk with a plurality of inclined planes is rotated in the liquid in the circumferential direction, the liquid dynamic pressure is generated by the liquid wedge (the working principle of the dynamic pressure thrust bearing), so that the workpiece in the retaining ring floats off the surface of the disk. The workpiece is polished by powder particles in a floating gap. No frictional heat and tool wear during processing, the standard plane does not change, so the precision of the workpiece surface can be repeated. The method is mainly used for polishing semiconductor substrates and various functional ceramic materials and optical glass, and can perform multi-chip processing at the same time. By processing the 3" diameter silicon wafer in this way, a flatness of 0.3 μm and a surface roughness of Ra1 nm can be obtained.
4. Non-contact chemical polishing An ordinary disc type chemical polishing method is to remove a chemical reaction product generated on a surface of a workpiece by supplying a chemical polishing liquid to the polishing surface to slide relative to the surface to be processed. . This kind of processing is mainly based on chemical corrosion and supplemented by mechanical action, also known as chemical mechanical polishing. Hvdroplan Polishing is a new chemical polishing method in which the workpiece and the polishing disc are not in contact with each other and no abrasive is used. It floats the workpiece substrate from the surface of the polishing disk by means of fluid pressure, and polishes the liquid using a corrosive liquid as a working fluid. The water surface sliding polishing method was developed for polishing compound semiconductor substrates such as GaAs and lnP, and the polishing apparatus is shown in Figures 3-14. The semiconductor substrate to be processed was adsorbed on the bottom surface of a crystal optical plate having a diameter of 100 mm as a workpiece holder. The edge of the crystal plate is tapered and connected to the polishing device by a pulley. The height of the substrate can be adjusted with an adjustment nut (adjustment range is within 125 μm). The etching solution is injected near the center of the polishing disc. When the polishing disc is rotated at 1200r/min, the crystal plate is rotated at 1800r/min by the liquid friction force, and the crystal plate is floated by the dynamic pressure to complete the polishing disc to the workpiece. Non-contact chemical polishing of the surface. The working fluid for water surface sliding polishing is a mixture of methanol, glycol and bromine. Methanol and bromine are effective corrosive solutions for GaAs and InP, and glycol has the effect of adjusting the viscosity of the liquid.
5. Cutting, grooving and end face polishing Non-contact end face polishing can be used to mirror the wall surface of the groove and the vertical column axis. This is difficult to achieve with traditional polishing methods. A schematic diagram of the end face non-contact mirror polishing device is shown in Figure 3-15. The tool and the workpiece do not touch each other. The high-speed rotating tool drives the particles to impact the workpiece to form a groove or cut, and then the same tool is used to polish the same position several times to realize the mirror polishing of the section. The processed surface roughness is lower than Ra3nm, and there is no lamination defect of hot oxygen. The method can be used for mirror polishing of end faces of optical fiber line parts having a diameter of about 0.1 mm and cutting of precision components.
Aloe Vera Microfiber Fabrics Item
Aloe Vera Fabric,Aloe Vera Textile,Aloe Vera Cotton,Aloe Vera Fiber Fabric
Changxing Zhongyuan Textile Co.,Ltd. , https://www.zyhometextile.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)